問1
(1)の答
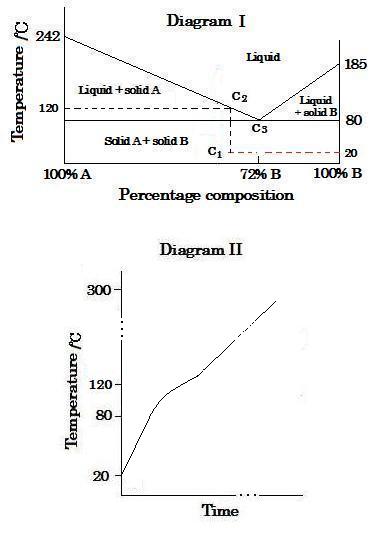
短時間にわたっての温度変化は, 下図Iを参照して,下図IIのように表わされる。熱がその固体混合物に加えられるとき, 固体の温度は時間に対して20℃から80℃(共有点)で直線的に上昇し, 混合物は固体状態のままである。
80℃から約140℃の間の温度では, 固体混合物の一部が温度増加で溶解する。液体の成分はBがより濃縮される。混合物は約140℃で溶融を完遂し, 温度は約140℃から300℃まで直線的に上昇する。もし混合物が徐々に加熱されるならば, 120℃の一定温度で完全に溶解する。
 (image566)
(image566)●1 2つの物質が, 2つの固体として存在するとき, その状態図は, 普通温度が圧力一定で変化するにつれ, 特有の安定相から成り立つ。他の物質を加えると, どちらかの内の成分の融点を降下させる。そこで合金は特により低融の純金属の融点よりも低温でとけるようになる。
●2 成分 c1(60% B と 40% A)の固体混合物が加熱されるとき, 上図Iを参照して, 80℃の水平線に到達するまで固体状態のままで残る。そして80℃と120℃の間の温度で固体の一部が溶け始める, その120℃では混合物は短時間で上昇する温度に曝されるので, 120℃の一定温度で固定されない。混合物は, 低融点の純金属Aの融点, 185℃より低い温度, 約140℃で完全に溶融する。
●3 混合物のc3(28% A, 72% B)の点は80℃の温度で溶け始め, 純物質の融点と類似の挙動を示す共有混合物を形成する。この点は共有点と呼ばれている。
共有状態は純物質AやBと区別される。その理由はどちらかの成分を少し加えてもその融点を増加させるからである。顕微鏡実験では共有成分の固体は2つの成分の各々の微結晶から成立していることを示している。
Q1
Answer of (i)
The temperature change over a short period time is shown as the diagram II below, referring to the diagram I. When a heat is added to the solid mixtuer, the temperature of the solid mixture rises linearly from 20℃ to 80℃(the eutectic point), and the mixture remains in a solid state.
At a temperature between 80℃ and about 140℃, a part of the solid mixture melts with increasing in temperature. The composition of the liquid gets more concentrated in B. The mixture completes melting at about 140℃, and its temperature rises linearly from about 140℃ to 300℃. If the mixture is gradually heated, it will melt completely at the constant temperature of 120℃.
 (image566)
(image566)●1 When two substances are present, such as two solid, the phase diagram usually consists of specifying the stable phase as temperature is changed at constant pressure. Adding the other substance lowers the melting point of either component. So an alloy will typically melt at a lower temperature than the melting point of the lower-melting pure metal.
●2 When the solid mixture of composition c1(60% B and 40% A) is heated, referring to the diagram I above, it remains in a solid state until it reaches the horizontal line of 80℃. And a part of the solid begins to melt at a temperature between 80℃ and 120℃ where as the mixture is exposed to temperatures which rise over a short period time, so it is not fixed at the constant temperature of 120℃. The mixture completes melting at a lower temperature, about 140℃, than the melting point of the lower-melting pure metal A, 185℃.
●3 The point c3 (28% A, 72% B) of the mixture corresponds to the composition that begins to melt at the temperature of 80℃, and that forms the eutectic mixture which shows the similar behavior of pure substance in melting point. This point is called the eutectic point.
The eutectic state can be distinguished from pure A or pure B because adding a little of either component will increase its melting point. Microscopic examination shows that the solid with the eutectic composition consists of small individual crystals of the two components.
(ii)の答
上の図 I を参照して, 混合物のc3点 (28% A, 72% B) は共融成分に対応している。そこで, 熱が固体混合物に加えられるとき, その固体は80℃(共融点)の温度で溶融し始め, 共融点のその温度は全ての固体が溶けるまで時間に対して一定のままである。
Answer of (ii)
Referring to the diagram I above, the point c3(28% A, 72% B) of the mixture corresponds to the eutectic composition. So, when a heat is added to the solid mixture, the solid begins to melt at the temperature of 80℃ (the eutectic point), which remains constant against time until all the solid has melted.
(iii)の答 共融混合物
Answer of (iii) A eutectic mixture.
問2の答 0.356 (有効数字3桁)
そのプラグの組成は72%Bと28%Aから成る。そこで1000gのプラグがあるときAとBの物質量は, 相対原子量を使用して, 次のように計算される。
Aの物質量は,
280/127 = 2.20 (有効数字3桁)
そしてBの物質量は
720/181 = 3.98 (有効数字3桁).
そこでAのモル分率は
2.20/(2.20 + 3.98) = 0.356 (有効数字3桁).
Answer of Q2 0.356 (3 sig. figs)
The plug composition consists of 72% B and 28% A. So when there is 1000 g of the plug, the amounts of A and B in moles are calculated as follows, using the relative masses.
For the amount of A in moles,
280/127 = 2.20 (3 sig. figs)
and for the amount of B in moles,
720/181 = 3.98 (3 sig. figs).
So the mole fraction of A is
2.20/(2.20 + 3.98) = 0.356 (3 sig. figs).