問1
(i)の答
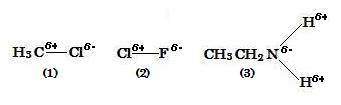
●1 H, C, N, Cl, および F の電気陰性度の値は,
H, 2.1 ; C, 2.5 ; N, 3.0 ; Cl, 3.0 ; F, 4.0
である。
●2 どんな原子でももう1つのより大きい電気陰性度の原子と結合するとき, 部分的な正電荷 (δ+) を持つことになる。電子密度はより高い電気陰性度の原子に引き寄せられる。
●1と●2を参照して, 化合物 (1) 中の原子の電気陰性度値の順序は C 2.5 < Cl 3.0 であるので, 結合 C-Cl においてC は部分的な正電荷 (δ+) で Cl は部分的な負電荷 (δ-) で帯電される。
化合物 (2) において, Cl 3.0 < F 4.0, そこで Clδ+―Fδ-.
化合物 (3) において, H 2.1 < N 3.0, そこで Nδ-―Hδ+.
Q1
Answer of (i)
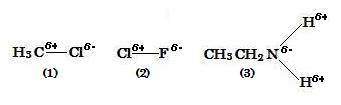 (image563)
(image563)●1 The electronegativity values of H, C, N, Cl, and F are,
H, 2.1 ; C, 2.5 ; N, 3.0 ; Cl, 3.0 ; F, 4.0.
●2 Any atom will have a partial positive charge (δ+) when it is bonded to another atom of greater electroneativity. Electron density is withdrawn from the atom with the greater electronegativity.
Referring to ●1 and ●2, as the order of electronegativity values of atoms in the compound (1) is 2.5 for C < 3.0 for Cl, C is charged with a partial positive (δ+) and Cl with a partial negative (δ-) in the bond, C-Cl.
In the compound (2), 3.0 for Cl < 4.0 for F, so Clδ+―Fδ-.
In the compound (3), 2.1 for H < 3.0 for N, so Nδ-―Hδ+.
(ii)の答
ある原子の電気陰性度は共有の電子対を引き寄せる能力の粗い物差しを意味する。そこで大きな電気陰性度の原子は結合の電子対の大きな分配を持ち, その電子密度はより大きくなり部分的負電荷δ-を伴なうことになる。
● 共有結合が同一でないふたつの原子間で存在するところでは, ふたつの原子の内ひとつは結合の電子対のより大きな分配を持つことになる。不均一な分配が起きるのは異なった原子が電子対に対して違った引力を持つからである。
ある原子の電気陰性度は共有の電子対を引き寄せる能力の粗い物差しを意味する。その電気陰性度は相対的量でポーリングスケールにおいてセシウムの 0.8 からフッ素の 4.0 まで測定されている。より大きな電気陰性度の原子は結合の電子対のより大きな分配をもつ。そこでその電子密度はより大きな電気陰性度の原子へ歪められる (いわゆるその近傍でより大きくなる)。
Answer of (ii)
The electronegativity of an atom gives a rough measure of its ability to attract a shared electron pair. So the atom with the greater electronegativity will have a larger share of the bonding pair of electrons, and its electron density will become higher with a partial negative δ-.
● Where a covalent bond exists between two atoms that are not identical, one of the two will have a greater share of the bonding pair of electrons. Unequal sharing happens because different atoms have different powers of attraction for electron pairs.
An electronegativity of an atom gives a measure of its ability to attract a shared electron pair. The electronegativity is a relative quantity and is measured on the Pauling scale, ranging from 0.8 for caesium to 4.0 for fluorine. The atom with the greater electronegativity will have a larger share of the bonding pair of electrons. So the electron density will be skewed toward (i.e. higher near) the more electronegativity atom.
問2
(i)の答 120
●1 水素結合は分子間力の中で最も強い。それは共有結合の強度の約 5%を占め得る引力である。水素結合は分子間で形成しそれらの分子においては小さくて大きい電気陰性度の元素のフッ素, 酸素, あるいは窒素のひとつに結合された水素原子を含む。
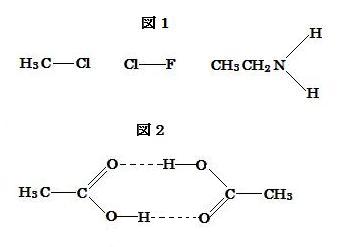
●2 ●1と図2を考慮すると, ベンゼン中のエタン酸の粒子は二量体を形成しそれは水素結合から成る 2個の酸素原子の各々に結合した 2個の水素原子を持つ。そこでエタン酸の見かけの相対分子量, いわゆる, 二量体 (CH3COOH)2 の分子量は次のように計算される。
(CH3COOH)2 の見かけの分子量 = 2×(2×12 + 4×1.0 + 2×16)
= 120
Q2
Answer of (i) 120
●1 Hydrogen bonding is the strongest of the intermolecular forces. It is a force of attraction that can have about 5% of the strength of covalent bond. Hydrogen bonds form between molecules that contain a hydrogen atom bonded to one of the small, highly electronegative elements fluorine, oxygen, or nitrogen.
●2 Considering ●1 and the diagram 2, an ethanoic acid particle in benzene will form a dimer that has two hydrogen atoms bonded to each of two oxygen atoms, consisted of hydrogen bonds. So the apparent relative molecular mass of ethanoic acid, that is, of the dimer, (CH3COOH)2 , is calculated as follows.
The apparent molecular mass of (CH3COOH)2 = 2×(2×12 + 4×1.0 + 2×16)
= 120
(ii)の答
名称 : 水素結合
エタン酸分子は分子中の元素の電気陰性度値の違いのためにヒドロキシル基中のδ+ 水素原子とカルボニル基中のδ- 酸素原子を形成する。それ故, カルボニル基のその酸素原子は水素結合によって近接のもうひとつの分子と結合し, そこで二量体を形成しそれは図2に示されるように2つのδ+ 水素原子が2つのδ- 酸素原子と結合している。
Answer of (ii)
Name : Hydrogen bond
Ethanoic acid molecule forms δ+ hydrogen atom in hydroxyl and δ- oxygen atom in carbonyl because of differences in the electronegativity values for elements in the molecule. The oxygen atom of carbonyl is therefore bonded with nearby another molecule by the hydrogen bond, so a dimer forms that has two δ+ hydrogen atoms bonded to each of two δ- oxygen atoms as shown in the diagram 2.
(iii)の答
水分子中の酸素原子 O とエタン酸分子中のメチル基の炭素原子 C との間に電気陰性度の違いが存在する(3.5 と2.5)。 結果として, 水分子中の水素原子 H の分極正電荷δ+ はエタン酸分子のヒドロキシル基中の水素原子 H のδ+ より大きい。
それ故, エタン酸中のカルボニル基 CO の酸素原子 O は水かエタン酸の分子と水素結合によって結合され, そしてその結合(…)の強度の順序は次のようになる。
OH-H…O=C(OH)CH3 > CH3(CO)O-H…O=C(OH)CH3
上の強度の順序を考慮すると, 水中のエタン酸に対しての図2で示されるような二量体を形成することは難しい。したがって液体の水中ではほとんど解離したエタン酸イオンが存在しその相対分子量は約 60 で, 問2(i)で計算された値の約半分である。
●1 液体の水において, 水素結合は, δ+ の水素原子が近接分子の酸素原子上の孤立電子対を引き付けるので, 形成する。水分子は凝集してかたまりに成り, それらは衝突の結果として絶えず生滅している。
●2 水素結合の三次元網目状構造は規則的で空隙のある格子構造で水分子を保持している。各酸素原子は2つの共有結合と2つの水素結合を形成する。
●3 水素, 炭素および酸素の電気陰性度値は H 2.1, C 2.5, および O 3.5 である。
水分子中の酸素原子 O とエタン酸分子中のメチル官能基の炭素原子 C との間に電気陰性度の違いが存在する(3.5 と2.5)。 結果として, 水分子中の水素原子 H の分極正電荷δ+ はエタン酸分子のヒドロキシル基中の水素原子 H のδ+ より大きい。
それ故, エタン酸中のカルボニル基 CO の酸素原子 O は水かエタン酸の分子と水素結合によって結合され, そしてその結合(…)の強度の順序は次のようになる。
OH-H…O=C(OH)CH3 > CH3(CO)O-H…O=C(OH)CH3
●4 上の●3を考慮すると, エタン酸が水に溶けるときエタン酸に対しての図2で示されるような二量体を形成することは難しい。したがって, 液体の水中ではほとんど解離したエタン酸のイオンが存在しその相対分子量は約 60 で, 問2(i)で計算された値の約半分である。
Answer of (iii)
There is a difference in electronegativity between oxygen atom O in water molecule and carbon atom C of methyl in ethanoic acid molecule(3.5 and 2.5). As a result, the partial positive charge δ+ of hydrogen atom H in water molecule is larger than the δ+ of hydrogen atom H in hydroxyl of ethanoic acid molecule.
An oxygen atom O of carbonyl CO in ethanoic acid is therefore bonded by hydrogen bond with molecules of water or ethanoic acid, and the strength order of the bond (…) is as follows.
OH-H…O=C(OH)CH3 > CH3(CO)O-H…O=C(OH)CH3
Considering the strength order above, it is difficult to form the dimers as shown in the diagram 2 for ethanoic acid in water. Accordingly there exist almost ethanoic acid ions dessociated in liquid water and the relative molecular mass is about 60, about half the value calculated in Q2(i).
●1 In liquid water, hydrogen bonds form as δ+ hydrogen atoms attract the lone pairs on oxygen atoms of nearby molecules. Water molecules group together in clumps, which are constantly losing and gaining molecules as a result of random collisions.
●2 A three-dimensional network of hydrogen bonds holds water molecules in a regular and open lattice structure. Each oxygen atom forms two covalent bonds and two hydrogen bonds.
●3 The electronegativity values for hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen are H 2.1, C 2.5, and O, 3.5.
There is a difference of electronegativity between oxygen atom O in water molecule and carbon atom C of methyl function in ethanoic acid molecule(3.5 and 2.5). As a result, the partial positive charge δ+ of hydrogen atom H in water molecule is larger than the δ+ of hydrogen atom H in hydroxyl of ethanoic acid molecule.
An oxygen atom O of carbonyl CO in ethanoic acid is therefore bonded by hydrogen bond with molecules of water or ethanoic acid, and the strength order of the bond (…) is as follows.
OH-H…O=C(OH)CH3 > CH3(CO)O-H…O=C(OH)CH3
●4 Considering ●3 above, it is difficult to form the dimers as shown in the diagram 2 for ethanoic acid when ethanoic acid is dissolved in water. Accordingly, there exist almost ethanoic acid ions dissociated in liquid water and the relative molecular mass is about 60, about half the value calculated in Q2(i).
 (image562)
(image562)